|
| Query: apes and monkeys | Result: 5th of 48 | |
New World Monkey (Parvorder: Platyrrhini) - Wiki
| Subject: | New World Monkey (Parvorder: Platyrrhini) - Wiki
| |
| Resolution: 900x557
File Size: 272442 Bytes
Date: 2007:10:08 14:39:54
Upload Date: 2007:10:08 14:43:59
|
New World Monkey (Parvorder: Platyrrhini) - Wiki
New World monkey
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
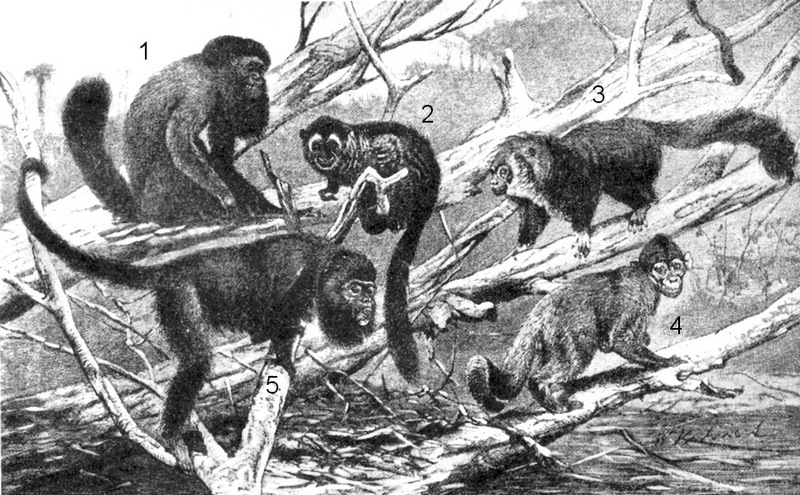
[Photo] Primates:New World Monkeys. 1. Chiropotes satanas 2. Pithecia monachus 3. Aotus trivirgatus 4. Alouatta caraya 5. Cebus apella. License: public domain
The New World monkeys are the four families of primates that are found in Central and South America: Cebidae, Aotidae, Pitheciidae and Atelidae. The four families are ranked together as the Platyrrhini parvorder. They differ from other groupings of monkeys and primates, such as the Old World monkeys and the apes.
About 40 million years ago the Simiiformes infraorder split into parvaorders Platyrrhini (New World monkeys???in South America) and Catarrhini (apes and Old World monkeys???in Africa). The Platyrrhini are currently conjectured to have migrated across the Atlantic Ocean to South America on a raft of vegetation similar to the vast pieces of floating mangrove forest that storms occasionally break off from the tropical African coast. At that time the Atlantic Ocean was less than the present 2800km wide.
Characteristics
New World monkeys differ slightly from Old World monkeys in several aspects. The most prominent difference is the nose, which is the feature used most commonly to distinguish between the two groups. The scientific name for the New World monkeys, Platyrrhini, means "flat nosed". The noses of New World monkeys are flatter, with side facing nostrils, than the narrow noses of the Old World monkeys. Platyrrhines also differ from Old World monkeys in that they have twelve premolars instead of eight. Most New World monkeys have long tails that are often prehensile. Many New World monkeys are small and almost all are arboreal, so knowledge of them is less comprehensive than that of the more easily observed Old World monkeys. Unlike most Old World monkeys, many New World monkeys form monogamous pair bonds, and show substantial paternal care of young.
Classification
ORDER PRIMATES
Suborder Strepsirrhini: lemurs, lorises, etc.
Suborder Haplorrhini: tarsiers, monkeys and apes
Infraorder Tarsiiformes
Family Tarsiidae: tarsiers
Infraorder Simiiformes
Parvorder Platyrrhini: New World monkeys
Family Cebidae: marmosets, tamarins, capuchins and squirrel monkeys
Family Aotidae: night or owl monkeys (douroucoulis)
Family Pitheciidae: titis, sakis and uakaris
Family Atelidae: howler, spider and woolly monkeys
Parvorder Catarrhini: Old World monkeys, apes and humans
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_World_monkey
| The text in this page is based on the copyrighted Wikipedia article shown in above URL. It is used under the GNU Free Documentation License. You may redistribute it, verbatim or modified, providing that you comply with the terms of the GFDL. |
|
^o^
Animal Pictures Archive for smart phones
^o^
|
|

