|
| Query: Birds | Result: 1439th of 32685 | |
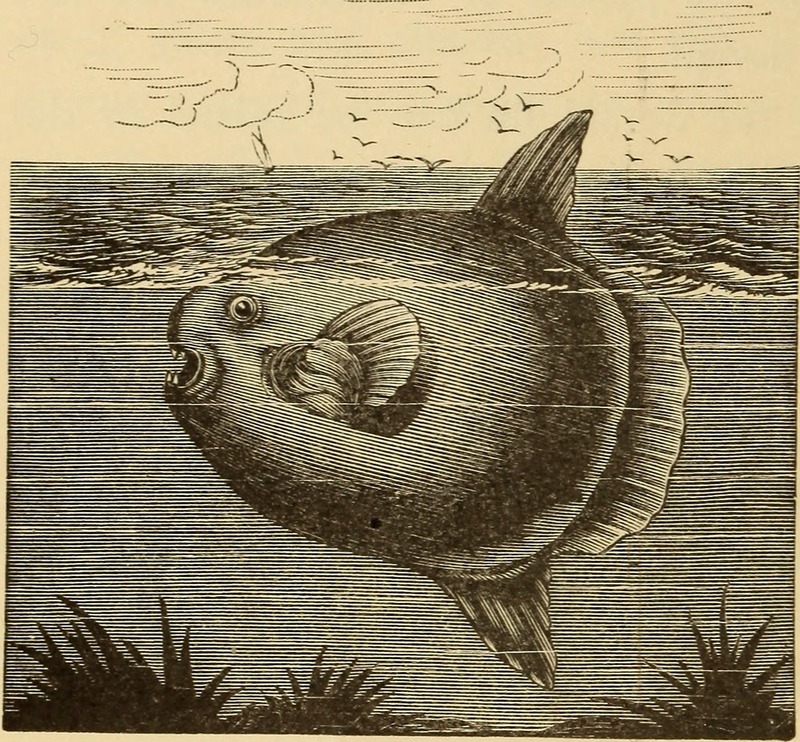
ocean sunfish, common mola (Mola mola)
| Subject: | ocean sunfish, common mola (Mola mola)
| | Poster: | Wiki Photos (---@---.---)
| |
| Resolution: 1540x1428
File Size: 765647 Bytes
Upload Date: 2017:09:03 22:22:15
|
ERROR : Server Busy(-1105)
ERROR : Server Busy(-1105)
ocean sunfish, common mola (Mola mola)
Fig. 2. — Sunfish.
Title: Half hours with fishes, reptiles, and birds
Year: 1906 (1900s)
Authors: Charles Frederick Holder, 1851-1915
Subjects: Zoology
Source book page: https://archive.org/stream/halfhourswithfis00hold/halfhourswithfis00hold#page/n17/mode/1up
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Half_hours_with_fishes,_reptiles,_and_birds_(1906)_(14749031211).jpg
The ocean sunfish or common mola (Mola mola) is the heaviest known bony fish in the world. The ocean sunfish is native to tropical and temperate waters around the globe. Mola mola resembles a fish head with a tail, and its main body is flattened laterally. |
^o^
Animal Pictures Archive for smart phones
^o^
|
|