|
| 질의: north african elephant-shrew | 결과: 2번째/4 | |
Elephant Shrew (Family: Macroscelididae) - Wiki
| 제목: | Elephant Shrew (Family: Macroscelididae) - Wiki
| |

| 해상도: 622x504
파일크기: 160634 Bytes
촬영일: 2007:04:09 15:23:17
사진기: DSC-T10 (SONY)
F number: f/3.5
Exposure: 10/400 sec
Focal Length: 633/100
등록시간: 2007:09:20 18:37:29
|
Elephant shrew
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
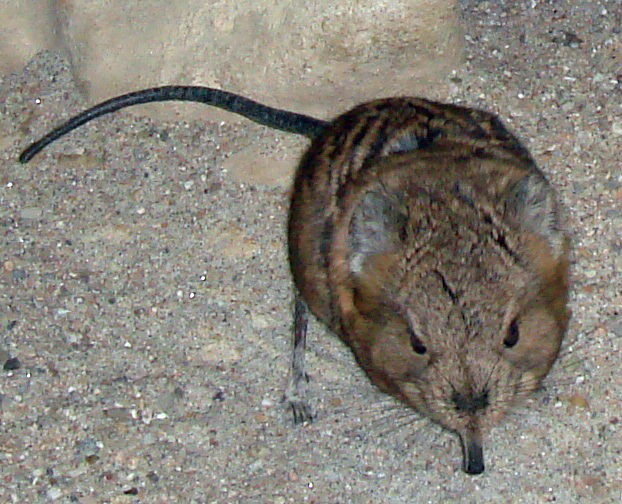
[Photo] Photo of an elephant shrew taken by ElinorD in Frankfurt Zoo on 9 April 2007. | Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled "GNU Free Documentation License". |
The small insectivorous mammals native to Africa known as elephant shrews or jumping shrews belong to the Macroscelididae family, in the order Macroscelidea. Their traditional common English name comes from a fancied resemblance between their long noses and the trunk of an elephant, and an assumed relationship with the true shrews (family Soricidae) in the order Insectivora. As it has become plain that the elephant shrews are unrelated to the shrews, some people prefer to call them sengis, a term derived from the Bantu languages of Africa.
The 15 species vary in size from about 100 mm to almost 300 mm, from just under 50 g to over 500 g. The Short-eared Elephant Shrew has an average size of 150 mm. All are quadrupedal with rather long legs for their size, and although the size of the trunk varies from one species to another, all are able to twist it about in search of food. Their life span is about 2 or 3 years. Their diet is largely insects and other small creatures, particularly beetles, spiders, worms, ants, and termites, mostly gleaned from leaf litter, but they also take seeds and some green shoots. The Rhynchocyon species also dig small conical holes in the soil, bandicoot style.
They are widely distributed across the southern part of Africa, and although common nowhere, can be found in almost any type of habitat, from the Namib Desert to boulder-strewn outcrops in South Africa to thick forest. One species, the North African Elephant Shrew, remains in the semi-arid, mountainous country in the far north-west of the continent.
Although mostly diurnal and very active, they are difficult to trap and very seldom seen: sengis are wary, well camouflaged, and adept at dashing away from threats. Several species make a series of cleared pathways through the undergrowth and spend their day patrolling them for insect life: if disturbed, the pathway provides an obstacle-free escape route.
The evolutionary history of the sengis has long been obscure. At various stages, they have been classified with the shrews and hedgehogs as part of the Insectivora; regarded as distant relatives of the ungulates; grouped with the treeshrews; and lumped in with the hares and rabbits in Lagomorpha. Recent molecular evidence, however, weakly supports a superorder Afrotheria which unites tenrecs, and golden moles with certain ungulates or mammals that have been presumed to be ungulates, including hyraxes, sirenians, aardvarks and elephants, as well as the elephant shrews.
However this arrangement is not supported by good anatomical evidence and although the relationship of the golden moles to tenrecs is quite likely and the relationship between hyraxes, sirenians and elephants is also well accepted, anatomically these two groups of mammals are different from one another and evidence suggests that the odd-toed ungulates are related to the African ungulates. Although the dentition of elephant shrews suggests that they might be ungulates their overall morphology has similaritites to the gnawing mammals.
ORDER MACROSCELIDEA
Family Macroscelididae
Genus Elephantulus
Short-snouted Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus brachyrhynchus
Cape Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus edwardii
Dusky-footed Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus fuscipes
Dusky Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus fuscus
Bushveld Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus intufi
Eastern Rock Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus myurus
Somali Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus revoili
North African Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus rozeti
Rufous Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus rufescens
Western Rock Elephant Shrew, Elephantulus rupestris
Genus Macroscelides
Short-eared Elephant Shrew, Macroscelides proboscideus
Genus Petrodromus
Four-toed Elephant Shrew, Petrodromus tetradactylus
Genus Rhynchocyon
Golden-rumped Elephant Shrew, Rhynchocyon chrysopygus
Checkered Elephant Shrew, Rhynchocyon cirnei
Black and Rufous Elephant Shrew, Rhynchocyon petersi
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elephant_shrew
| The text in this page is based on the copyrighted Wikipedia article shown in above URL. It is used under the GNU Free Documentation License. You may redistribute it, verbatim or modified, providing that you comply with the terms of the GFDL. |
|
 |

|

|
north african elephant-shrew
2/4 |

|
 |
^o^
동물그림창고 똑똑전화 누리집
^o^
|
|

